#161
Introduction:-

Business strategic planning is like the roadmap for a company’s future. It involves setting goals, defining strategies, and outlining steps to achieve those goals. It’s critical because it helps a company stay focused, adapt to changes, and make informed decisions.
In EHS (Environment, Health, and Safety) functions, strategic planning is equally crucial. It ensures that the organization prioritizes safety, health, and environmental sustainability in its long-term objectives. By aligning EHS goals with overall business strategy, companies can prevent accidents, reduce risks, and enhance their reputation. Plus, it demonstrates a commitment to employee well-being and corporate responsibility.
So, in a nutshell, strategic planning in EHS keeps everyone safe, protects the environment, and supports the company’s overall success.
++++++
Strategic planning considers various factors to create a robust roadmap for success. Here are the key ones:
- Political Factors: These include government policies, regulations, and political stability. Changes in regulations can significantly impact business operations, so understanding and adapting to political dynamics is crucial.
- Social Factors: Social trends, cultural shifts, and demographic changes play a vital role. Understanding the preferences and behaviors of society helps businesses align their strategies with the needs and expectations of their customers and stakeholders.
- Economic Factors: Economic conditions, such as inflation rates, exchange rates, and market trends, directly influence business operations. Strategic planning needs to account for economic fluctuations and identify opportunities and risks within the market.
- Technical Factors: Advancements in technology, innovation, and infrastructure impact strategic decisions. Embracing technological developments can enhance efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness.
Considering these factors allows businesses to anticipate challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and stay relevant in a rapidly changing environment.
++++++
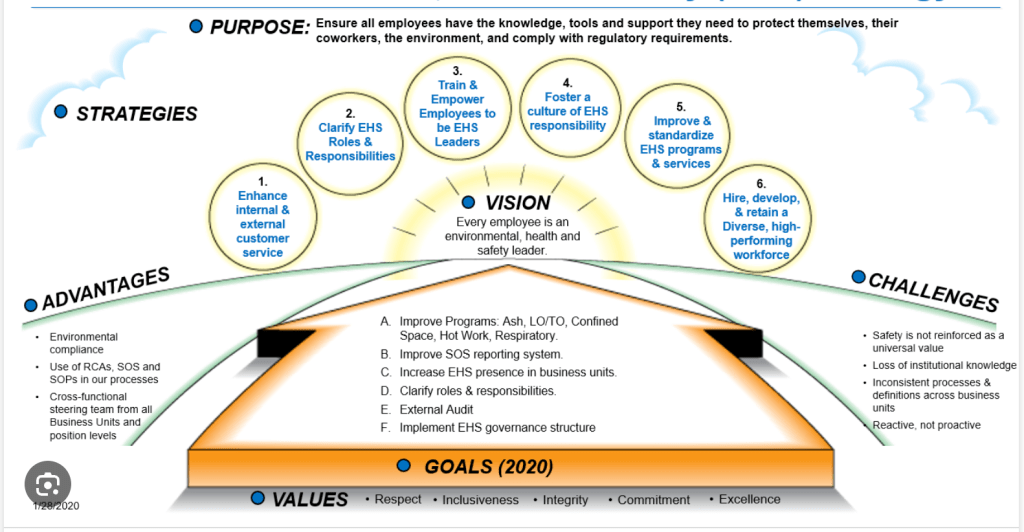
Strategic planning is like the compass that guides a company toward its mission, vision, and objectives. Here’s how it aligns:
- Company Values: Strategic planning ensures that the actions and decisions of the company align with its core values. It reinforces the importance of integrity, ethics, and responsibility in achieving long-term success.
- Mission: The mission statement defines the purpose and identity of the company. Strategic planning ensures that all initiatives and strategies contribute to fulfilling this mission, keeping everyone focused on the big picture.
- Objectives: Strategic planning translates high-level goals into actionable objectives. It establishes clear targets and milestones to measure progress and success. By aligning strategies with objectives, companies can prioritize initiatives and allocate resources effectively.

In essence, strategic planning serves as the bridge between a company’s values, mission, and objectives, guiding it toward its desired future state.
SWOT analysis is a valuable tool that links directly to strategic planning; Here’s how:
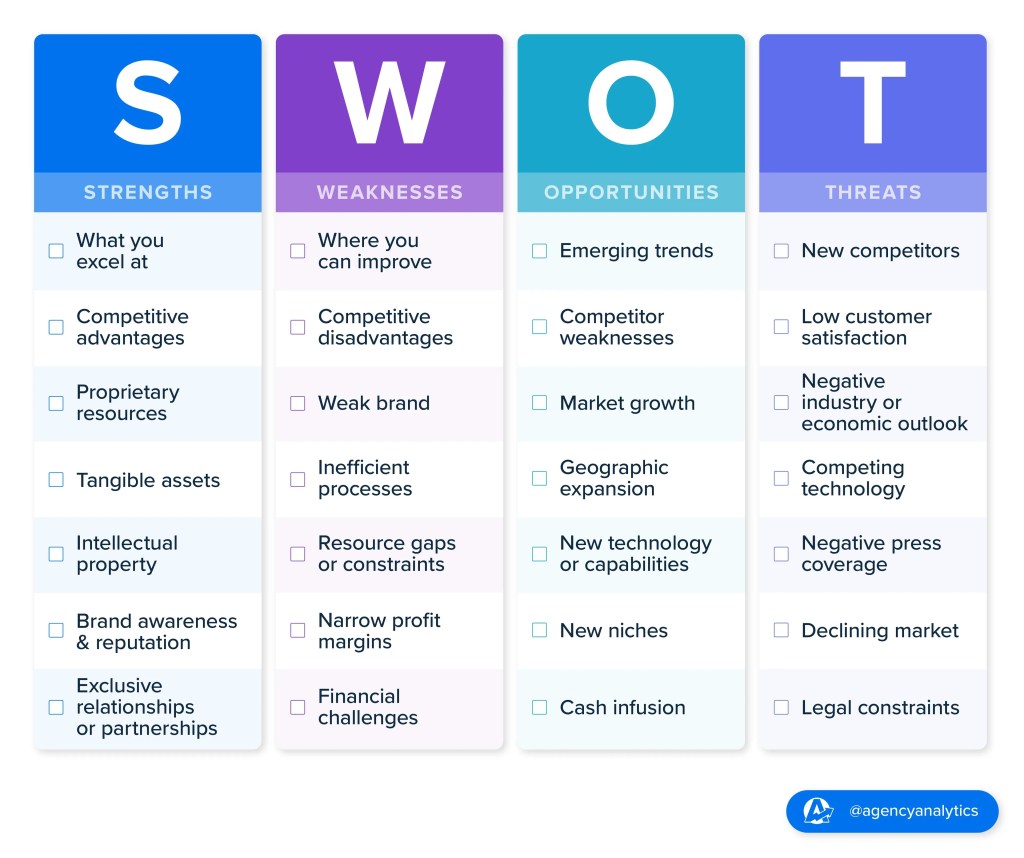
- Strengths: Identifying internal strengths allows organizations to leverage their advantages and capitalize on opportunities. Strategic planning involves aligning strengths with strategic objectives to enhance competitiveness and achieve sustainable growth.
- Weaknesses: Recognizing internal weaknesses helps organizations address areas of improvement and mitigate risks. Strategic planning involves developing strategies to overcome weaknesses, such as investing in training and development, process improvements, or strategic partnerships.
- Opportunities: Identifying external opportunities allows organizations to explore new markets, products, or partnerships. Strategic planning involves leveraging opportunities to drive innovation, expand market share, and achieve strategic goals.
- Threats: Recognizing external threats helps organizations anticipate challenges and mitigate risks. Strategic planning involves developing contingency plans, diversifying risk, and strengthening resilience to minimize the impact of threats on strategic objectives.
By conducting a SWOT analysis as part of the strategic planning process, organizations can gain valuable insights into their internal and external environment, inform strategic decision-making, and develop actionable strategies to achieve their goals effectively.
+++
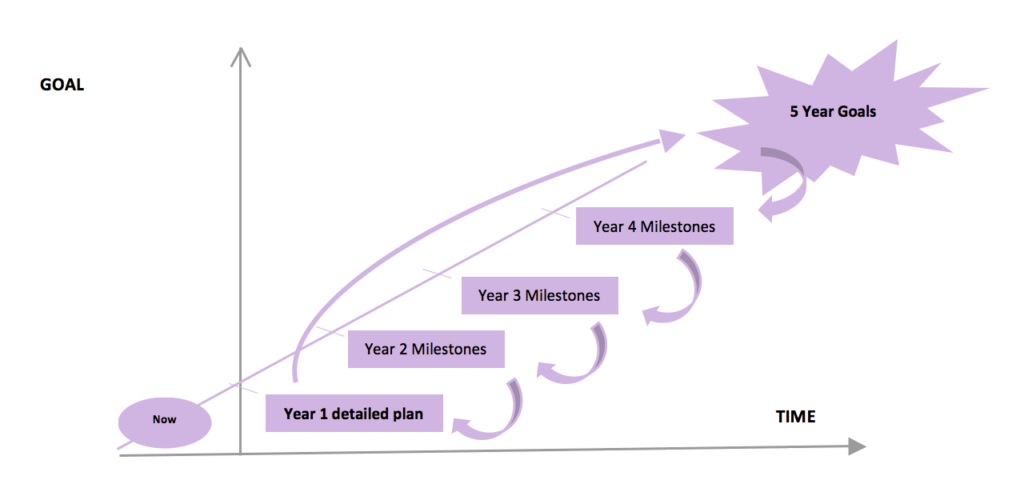
The ideal timeline for strategic planning typically spans around 3 to 5 years. Here’s a breakdown of how it might look:
- High-Priority Issues (Immediate to 2 years): Address critical challenges that require urgent attention. These could include regulatory compliance, safety improvements, or market shifts that demand immediate action.
- Medium-Priority Issues (2 to 3 years): Focus on medium-term goals and initiatives that support the company’s long-term vision. These may include investments in technology, talent development, or expansion into new markets.
- Low-Priority Issues (3 to 5 years): Identify longer-term opportunities and challenges that require strategic foresight. This could involve innovation projects, sustainability initiatives, or strategic partnerships aimed at securing future growth.
By categorizing issues based on priority and timeframe, companies can allocate resources effectively and ensure alignment with their strategic objectives. It’s like balancing short-term needs with long-term vision to sustain growth and success over time.
+++++
In EHS strategic planning, several factors come into play to ensure the safety, health, and environmental sustainability of the organization. Here’s how it might look:
- Regulatory Compliance: Keeping abreast of EHS regulations and ensuring full compliance is a top priority. Strategic planning involves identifying and addressing any gaps in compliance, as well as anticipating future regulatory changes.
- Risk Management: Assessing and mitigating risks related to workplace safety, health hazards, and environmental impact is crucial. Strategic planning includes developing risk management strategies and implementing preventive measures to minimize incidents.
- Employee Engagement and Training: Engaging employees in EHS initiatives and providing comprehensive training is essential. Strategic planning involves identifying training needs, implementing effective communication channels, and fostering a culture of safety and environmental responsibility.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Incorporating sustainability practices into business operations is becoming increasingly important. Strategic planning includes setting goals for reducing carbon footprint, conserving resources, and promoting eco-friendly practices.
- Emergency Preparedness: Planning for emergencies such as natural disasters, accidents, or hazardous spills is vital. Strategic planning involves developing emergency response plans, conducting drills, and ensuring readiness to handle any unforeseen events.
- Performance Measurement and Continuous Improvement: Monitoring EHS performance metrics and implementing feedback loops for continuous improvement is integral. Strategic planning includes establishing key performance indicators (KPIs), tracking progress, and adjusting strategies as needed.
By addressing these factors in EHS strategic planning, organizations can ensure a safe, healthy, and sustainable work environment while minimizing risks and meeting regulatory requirements.
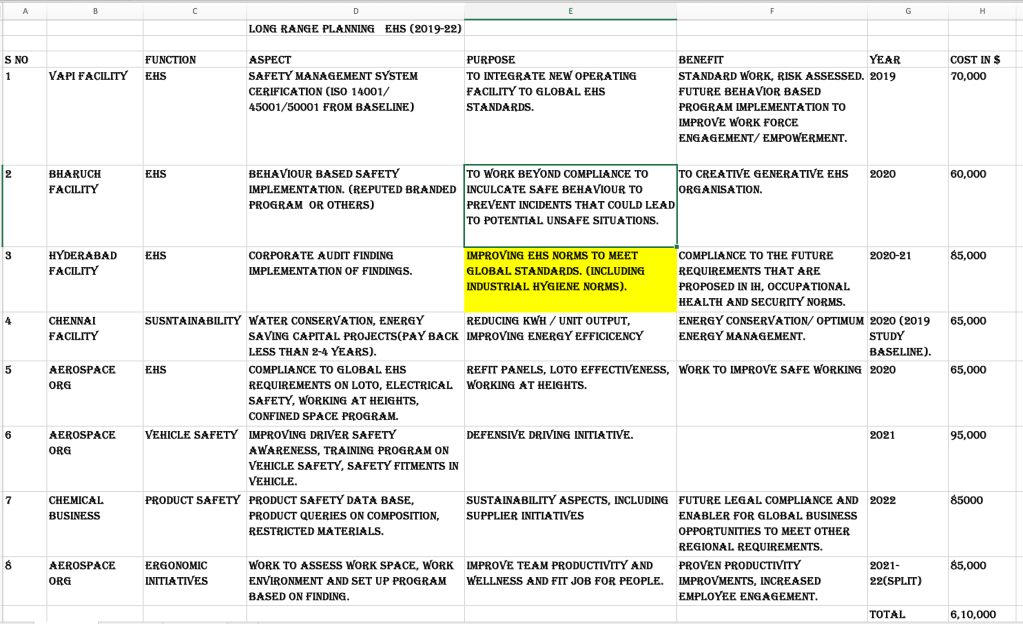
Funding anticipation for EHS strategic planning is essential to ensure the successful implementation of initiatives and achieve organizational goals. Here’s how it ties in:
- Budget Allocation: Anticipating funding needs allows organizations to allocate resources effectively to support EHS initiatives. By identifying key priorities and strategic objectives, companies can earmark funds for training, technology investments, infrastructure upgrades, and other critical areas.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Conducting cost-benefit analysis helps justify funding requests for EHS initiatives. By demonstrating the potential return on investment (ROI) in terms of improved safety, reduced risks, and regulatory compliance, organizations can secure funding support from stakeholders.
- Long-Term Planning: Anticipating funding requirements over the strategic planning period enables organizations to develop sustainable funding models. This may involve securing budget allocations from senior management, seeking external funding sources, or reallocating resources from non-essential areas to prioritize EHS initiatives.
- Collaboration with Finance: Collaborating with the finance department ensures alignment between EHS objectives and financial planning. By providing accurate cost estimates, financial projections, and ROI analysis, EHS professionals can effectively communicate funding needs and gain support from financial decision-makers.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Tracking expenditure against budget and reporting on the progress of EHS initiatives is critical for accountability and transparency. By regularly monitoring funding utilization and performance metrics, organizations can identify any discrepancies or inefficiencies and make timely adjustments to optimize resource allocation.
In summary, funding anticipation for EHS strategic planning involves aligning budget allocation with organizational priorities, conducting cost-benefit analysis, planning for long-term sustainability, collaborating with finance, and monitoring expenditure to ensure effective utilization of resources.
+++
Business risk management, including EHS (Environment, Health, and Safety), is intricately linked to strategic planning as it helps organizations identify, assess, and mitigate risks that could impact their long-term objectives. Here’s how they tie in:
- Risk Identification: Strategic planning involves identifying potential risks and opportunities that could affect the organization’s ability to achieve its goals. This includes risks related to EHS, such as workplace accidents, environmental incidents, regulatory non-compliance, and reputational damage.
- Risk Assessment: Once risks are identified, strategic planning incorporates a thorough assessment of their likelihood and potential impact. This allows organizations to prioritize risks based on their significance and develop strategies to mitigate or manage them effectively.
- Integration of Risk Mitigation Strategies: Strategic planning integrates risk mitigation strategies into the overall business strategy. This includes implementing preventive measures, establishing contingency plans, and allocating resources to address identified risks, including those related to EHS.
- Alignment with Objectives: Risk management ensures that EHS considerations are aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives. By embedding EHS practices into the strategic planning process, organizations can proactively address risks while pursuing their long-term goals.
- Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation: Strategic planning involves continuous monitoring of risks and performance metrics to track progress and identify emerging threats. This allows organizations to adapt their strategies in response to changing circumstances, including new EHS regulations, technological advancements, or shifts in market dynamics.
By integrating risk management, including EHS, into strategic planning, organizations can enhance resilience, minimize disruptions, and improve decision-making, ultimately contributing to long-term success and sustainability.
Here’s a comprehensive list of factors in EHS (Environment, Health, and Safety) that must be considered in strategic planning:
- Safety: Ensuring the safety of employees, contractors, and visitors is paramount. This includes implementing safety programs, conducting safety training, and establishing protocols for hazard identification and incident management.
- Product Stewardship: Managing the lifecycle of products to minimize environmental and health impacts. This involves considering factors such as raw material sourcing, product design, manufacturing processes, and end-of-life disposal or recycling.
- Facility Management: Maintaining safe and healthy working environments through proper facility design, Loss Prevention, maintenance, and emergency preparedness. This includes managing risks associated with hazardous materials, equipment, and infrastructure.
- Audits and Compliance: Conducting regular audits to assess compliance with EHS regulations and internal standards. This ensures that legal requirements are met, risks are identified, and corrective actions are implemented.
- Environmental Management: Managing environmental impacts such as air emissions, water discharges, waste generation, and resource consumption. This includes implementing pollution prevention measures, environmental monitoring, and sustainability initiatives.
- Industrial Hygiene (IH): Protecting the health and well-being of workers by assessing and controlling exposure to occupational hazards such as chemical, biological, and physical agents. This involves conducting exposure assessments, implementing engineering controls, and providing personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Business Continuity Planning: Ensuring the resilience of operations against potential disruptions, including natural disasters, Fires, supply chain disruptions, or public health emergencies. This includes developing contingency plans, crisis management protocols, and recovery strategies.
- Occupational Health: Promoting employee health and wellness through programs addressing ergonomic risks, occupational diseases, mental health, and workplace wellness initiatives.
- Training and Competency Development: Providing ongoing training and development opportunities to build EHS awareness, skills, and competency among employees at all levels of the organization.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging with internal and external stakeholders, including employees, communities, regulators, and NGOs, to foster transparency, collaboration, and trust in EHS management practices.
By considering these factors in strategic planning, organizations can effectively integrate EHS considerations into their overall business strategy, minimize risks, and achieve sustainable growth and performance.
++
People:- The people aspect is crucial in strategic management as they are the driving force behind the execution of strategies. Here’s how various elements related to people fit in:

- Retention: Strategic management involves ensuring the retention of top talent. By recognizing and rewarding high performers, providing opportunities for growth and development, and fostering a positive work culture, organizations can retain skilled employees who contribute to the achievement of strategic objectives.
- Risk: People-related risks, such as turnover, skills gaps, or lack of succession planning, can impact strategic execution. Strategic management includes identifying and mitigating these risks through measures such as talent retention strategies, succession planning, and cross-training to ensure continuity and stability.
- Competence Mapping: Strategic management involves mapping the competencies and skills required to execute strategic initiatives successfully. This includes identifying current skill gaps within the organization, developing training and development programs to address these gaps, and recruiting or reassigning talent to fill critical roles.
- Compensation: Compensation strategies play a significant role in aligning employee behaviors with strategic objectives. Strategic management involves designing compensation packages that incentivize desired performance outcomes, such as achieving strategic goals, driving innovation, or demonstrating leadership qualities.
Overall, integrating the people aspect into strategic management ensures that organizations have the right talent, with the right skills and motivation, to execute strategies effectively and achieve long-term success.
Conclusion:-
EHS strategic planning is key because it provides a clear path forward for a foreseeable future by prioritizing safety, health, and environmental sustainability within the organization. Here’s why it’s crucial:
- Risk Mitigation: EHS strategic planning helps identify and mitigate risks associated with workplace safety, health hazards, and environmental impact. By proactively addressing risks, organizations can prevent incidents, minimize liabilities, and safeguard their reputation.
- Compliance Assurance: Strategic planning ensures that the organization remains compliant with EHS regulations and standards. By staying ahead of regulatory requirements, organizations can avoid fines, penalties, and legal issues while maintaining a positive relationship with regulators and stakeholders.
- Resource Allocation: Strategic planning allows organizations to allocate resources effectively to support EHS initiatives. By prioritizing EHS investments based on strategic objectives, organizations can optimize resource utilization and maximize the impact of EHS programs.
- Long-Term Sustainability: EHS strategic planning considers the long-term impact of business operations on the environment, public health, and community well-being. By integrating sustainability practices into strategic decision-making, organizations can minimize their environmental footprint, foster social responsibility, and ensure long-term business viability.
- Employee Engagement and Morale: Strategic planning promotes a culture of safety, health, and environmental stewardship within the organization. By engaging employees in EHS initiatives and providing opportunities for participation and feedback, organizations can enhance employee morale, satisfaction, and retention.
Overall, EHS strategic planning provides a roadmap for organizations to navigate the complex landscape of environmental, health, and safety challenges while achieving their business objectives. By prioritizing EHS considerations in strategic decision-making, organizations can ensure a safer, healthier, and more sustainable future for all stakeholders.
B Karthik
13/3/24.

