#191
Introduction: Bridging the Gap Through Skill Development

In today’s competitive job market, Indian organizations face a significant challenge: a staggering 70% of graduates emerging from educational institutions are deemed unemployable. This alarming statistic reflects a broader issue with the current educational framework, which often leaves students lacking in critical areas such as attitude, behavior, knowledge, and essential skill sets. Consequently, organizations are frequently left with “no choice” but to hire employees who may be technically employable but require substantial development to become effective contributors.
In this context, developing and molding such employees to achieve results while keeping them motivated to learn and grow is a monumental task. This is where a robust skill development program comes into play, proving to be more vital than simply relying on knowledge, talent, or adherence to rules. Skill development goes beyond these foundations, equipping employees with the practical abilities necessary to perform their tasks safely and efficiently.
Implementing a comprehensive skill development program is not only crucial for enhancing safety and productivity but also serves as a potent employee retention strategy. Employees who are given the opportunity to develop their skills feel valued and are more likely to remain loyal to their organization. However, the challenge lies in devising and executing a coherent skill development strategy that involves input from all stakeholders, including managers and leaders at various levels within the organization.
Such a strategy demands a commitment to go above and beyond traditional approaches. It requires a concerted effort to identify skill gaps, provide targeted training, and foster a culture of continuous learning and improvement. Leaders must champion this initiative, demonstrating their dedication to employee growth and safety through consistent support and investment in skill development programs.
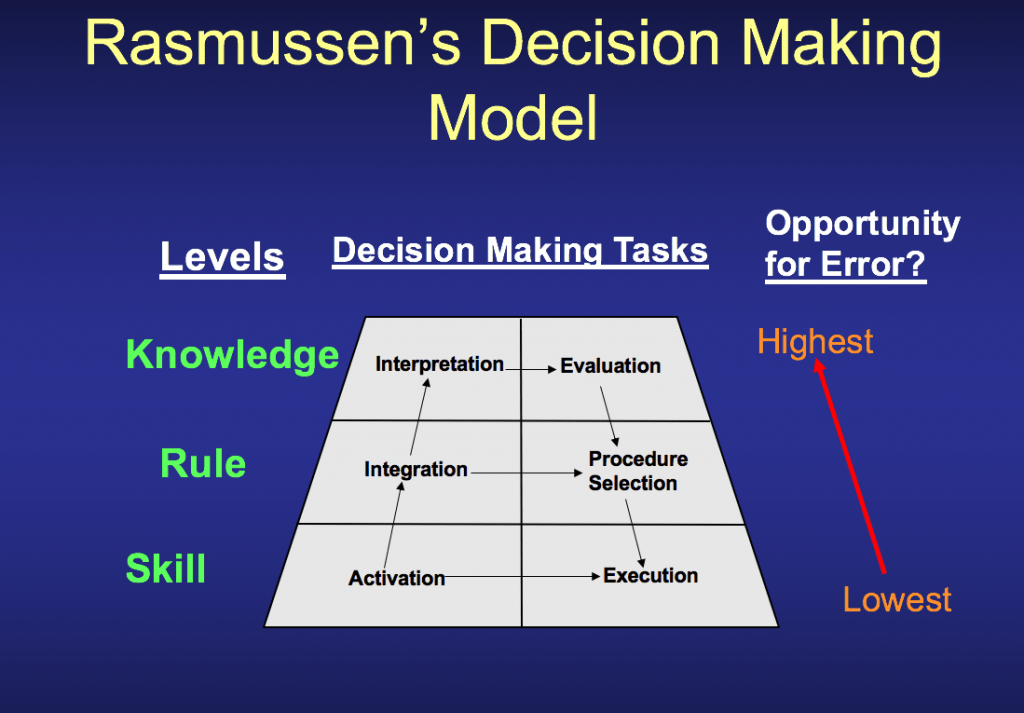
Why Skills Matter at Work to Achieve Performance
In the realm of Environment, Health, and Safety (EHS), and Operations, achieving top-notch performance is paramount. While talent, knowledge, and adherence to rules form the essential foundation of effective safety practices,Operational norms, it is skills that enable workers to execute tasks error-free and incident-free as well as for productivity.
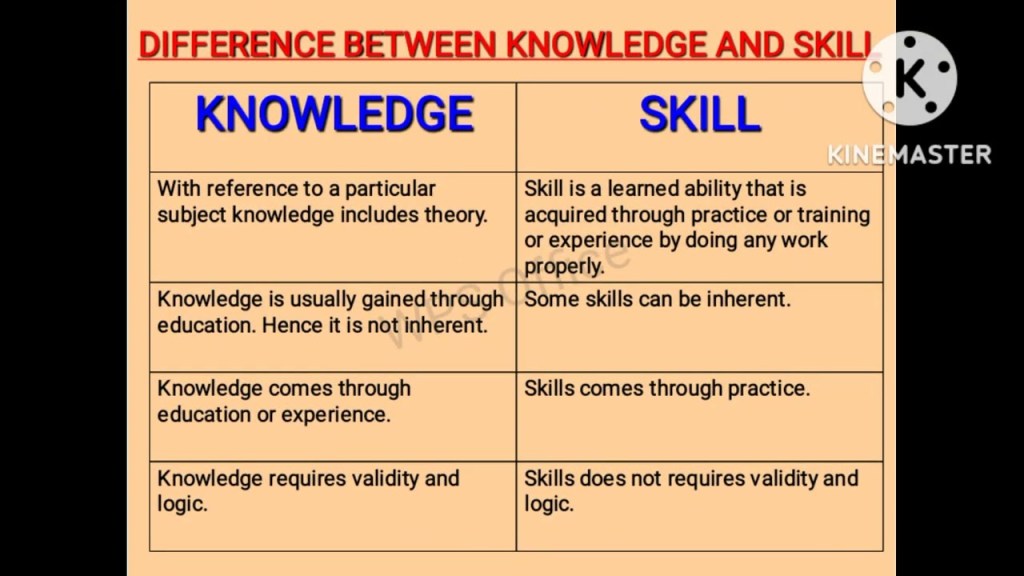
The Difference Between Talent, Knowledge, and Skills
Talent refers to the natural aptitude or ability that a person possesses. While talent can provide an edge, it is not always sufficient for ensuring safety.
Knowledge encompasses the theoretical understanding of safety procedures, guidelines, and regulations. It is crucial for knowing what needs to be done and why it is important.
Skills are the practical application of talent and knowledge. Skills are developed through training, practice, and experience, and they enable workers to perform tasks competently and safely.
In essence, while talent and knowledge provide the necessary framework, it is the development and application of skills that ensure tasks are performed correctly and safely.
Essential Skill Sets for Employees to Anticipate and Mitigate Potential Issues in the Workplace
To achieve a high level of productivity and safety, employees must develop specific skill sets that enable them to anticipate potential problems, recognize what has not yet occurred but could, and apply these insights effectively. Here are the key skill sets required for such proactive thinking:
1. Analytical Skills
Importance: Analytical skills allow employees to evaluate information critically and identify potential risks before they materialize.
How to Develop:
- Engage in problem-solving exercises.
- Take courses in critical thinking and data analysis.
- Regularly review and analyze past incidents to understand their causes and prevent future occurrences.
2. Situational Awareness
Importance: Being aware of the environment and potential hazards at all times helps in anticipating and mitigating risks.
How to Develop:
- Participate in safety drills and simulations.
- Practice mindfulness and observational techniques.
- Use checklists and standard operating procedures to remain vigilant.
3. Risk Assessment Skills
Importance: The ability to assess risks accurately helps in prioritizing actions to prevent incidents.
How to Develop:
- Undergo training in risk assessment methodologies such as HAZOP (Hazard and Operability Study) and FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis).
- Participate in risk assessment workshops.
- Work on real-life scenarios and case studies to apply risk assessment principles.
4. Problem-Solving Skills
Importance: Effective problem-solving skills enable employees to address potential issues quickly and efficiently.
How to Develop:
- Engage in regular problem-solving and brainstorming sessions.
- Learn various problem-solving frameworks like the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle.
- Practice solving hypothetical scenarios related to safety and productivity.
5. Communication Skills
Importance: Clear and effective communication is essential for reporting potential risks and coordinating preventive measures.
How to Develop:
- Participate in communication skills training.
- Practice active listening and clear, concise speaking.
- Engage in team-building exercises to improve collaborative communication.
6. Technical Skills
Importance: Technical proficiency ensures that employees can handle equipment and processes correctly, reducing the risk of errors.
How to Develop:
- Regularly update technical training and certifications.
- Stay informed about the latest technological advancements in the industry.
- Engage in hands-on practice and simulation-based learning.
7. Decision-Making Skills
Importance: The ability to make quick, informed decisions is crucial in preventing small issues from escalating into major problems.
How to Develop:
- Learn decision-making techniques and frameworks.
- Practice decision-making under pressure through simulations and drills.
- Reflect on past decisions to understand their outcomes and improve future choices.
8. Attention to Detail
Importance: Being meticulous helps in identifying minor issues that could lead to significant problems if overlooked.
How to Develop:
- Engage in tasks that require high precision and focus.
- Use checklists and standard procedures to ensure thoroughness.
- Practice quality control exercises to enhance attention to detail.
9. Continuous Learning and Adaptability
Importance: The ability to learn from past incidents and adapt to new information and techniques is vital for ongoing improvement in safety and productivity.
How to Develop:
- Foster a culture of continuous improvement and lifelong learning.
- Attend workshops, seminars, and training programs regularly.
- Encourage knowledge sharing and feedback within teams.
How Skills Can Be Acquired
Acquiring skills is a systematic process that involves:
- Training Programs: Structured training sessions, both theoretical and practical, tailored to the specific needs of the job.
- On-the-Job Experience: Practical exposure to real-world situations under supervision to apply learned concepts.
- Mentorship: Guidance from experienced workers to impart practical insights and techniques.
- Continuous Learning: Ongoing education and skill enhancement to keep up with new technologies and methods.
- Simulation and Drills: Regular drills and simulation exercises to prepare for emergency scenarios and improve response skills.
What Employees Need to Do
- Engage in Training: Actively participate in all training programs and seek additional learning opportunities.
- Practice Vigilance: Consistently apply safety skills and be alert to potential hazards.
- Communicate: Report safety concerns and near-misses promptly and clearly.
- Seek Feedback: Regularly ask for feedback to improve skills and performance.
- Stay Updated: Keep abreast of new safety practices and technologies.
What Leaders and Organizations Can Do
For Leaders:
- Promote a Safety Culture: Lead by example and foster an environment where safety is a core value.
- Provide Resources: Ensure employees have access to necessary training, tools, and PPE.
- Encourage Reporting: Create a non-punitive environment where employees feel comfortable reporting hazards and incidents.
- Recognize and Reward: Acknowledge and reward safe practices and skill development efforts.
For Organizations:
- Develop Comprehensive Training Programs: Implement regular and comprehensive training programs that cover all aspects of safety.
- Invest in Technology: Utilize technology for training, monitoring, and improving safety practices.
- Create a Skill Development Plan: Establish a clear path for skill acquisition and career development related to safety.
- Evaluate and Improve: Regularly assess the effectiveness of training programs and make necessary improvements.

Embracing Skill Enhancement to Get Work Done
Organizations must recognize that skill enhancement is an ongoing process. By investing in continuous training and development, fostering a culture that values safety, and providing the necessary resources and support, organizations can significantly enhance safety performance. Leaders must champion this approach, ensuring that employees at all levels are equipped with the skills needed to perform their tasks safely and effectively.

Karthik
17/6/24. 1700 Hrs.

