#192
Gen Z (Born 1996 and after), Millenials 1980-1995)

Strategies for Operational Leaders in Manufacturing and Supply Chain
Introduction
The Indian workforce under the age of 40, particularly those who joined after 2004, represents a significant shift in workplace dynamics and culture. These individuals, often referred to as Millennials and Gen Z, bring distinct characteristics, expectations, and values to their professional lives. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected through technology, the challenges and opportunities they face are not unique to India but resonate globally. This article explores the personal work styles, professional interactions, societal views, work-life balance, and advocacy for DEI (Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion) and mental health among this demographic. Additionally, it examines how leaders, managers, organizations, and HR departments can effectively engage and support this workforce.
Understanding the New Workforce
To manage the younger workforce effectively, operational leaders must first understand their characteristics:
- Technological Fluency: This generation is comfortable with technology and expects its integration into everyday work processes.
- Flexibility and Work-Life Balance: They value flexible work hours and the ability to balance personal and professional lives.
- Purpose and Engagement: They seek meaningful work and engagement, often aligning themselves with companies that have a clear purpose and values.
- Continuous Feedback: They thrive on regular feedback and development opportunities.

Personal Style of Work
The younger Indian workforce values flexibility and autonomy in their work. They often prefer project-based roles over traditional, hierarchical structures. This cohort is characterized by:
- Tech-Savviness: Growing up in the digital age, they are adept at using technology to enhance productivity and streamline processes.
- Collaborative Approach: They favor teamwork and collaborative efforts over isolated tasks, leveraging diverse perspectives to achieve innovative solutions.
- Purpose-Driven Work: They seek meaning in their work, often aligning with organizations that have a strong sense of purpose and social responsibility.
Professional Interaction
In terms of professional interactions, the younger workforce displays:
- Open Communication: They appreciate transparent and open communication channels with their peers and superiors. This generation is more likely to voice their opinions and expect to be heard.
- Networking Skills: With strong networking capabilities, they use platforms like LinkedIn to connect with industry leaders, peers, and potential mentors.
- Feedback Orientation: Regular feedback and constructive criticism are crucial for their professional growth. They value continuous learning and development opportunities.
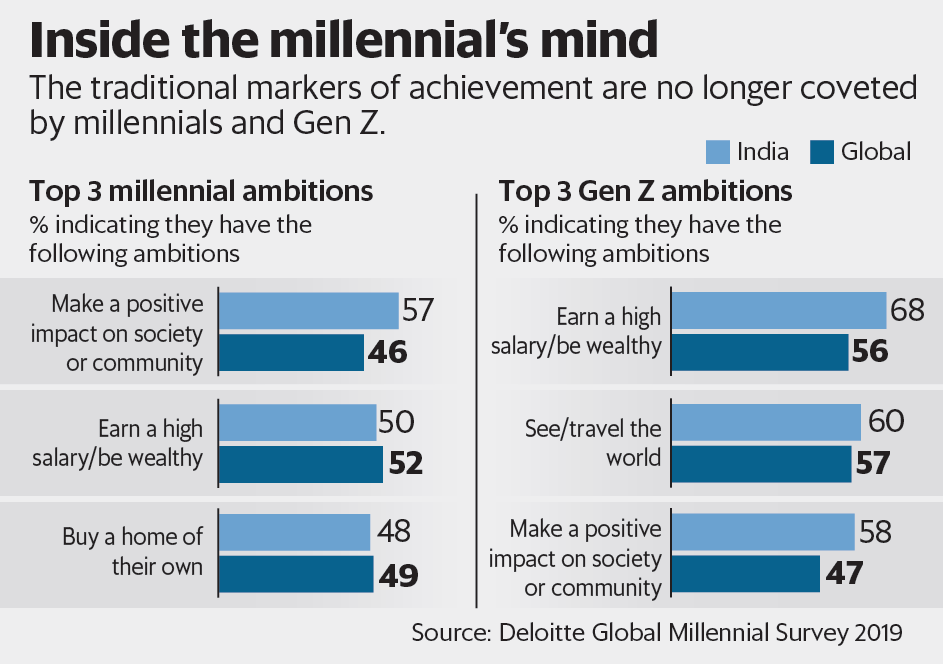
View of Society and Work
This generation’s view of society and work diverges significantly from previous generations:
- Work-Life Integration: Unlike the older generations who maintained a clear distinction between work and personal life, the younger workforce prefers integration. Flexible working hours and remote work options are highly valued.
- Social Responsibility: They are more socially conscious, often supporting environmental sustainability, social justice, and ethical business practices.
- Mental Health Awareness: There is a strong emphasis on mental health and well-being, with an expectation that employers will provide support and resources.

Vocal Expressions on Disagreements
The younger workforce is not hesitant to express their disagreements on various issues:
- Advocacy for Change: They actively advocate for changes they believe in, whether it’s workplace policies, societal issues, or political matters.
- Utilization of Social Media: Social media platforms are a common medium for expressing their views and rallying support for causes.
- Demand for Inclusion: They demand inclusivity and diversity in the workplace, challenging traditional norms and practices that may be outdated or discriminatory.

Focus on DEI and Mental Health
Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) and mental health are paramount for this generation:
- Inclusive Workplaces: They expect workplaces to be inclusive and diverse, reflecting a broad range of backgrounds and experiences.
- Support for Mental Health: They advocate for mental health support, seeking workplaces that provide resources such as counseling services, stress management programs, and a supportive environment.
Tech Savviness
Their proficiency with technology is a significant asset:
- Adoption of New Technologies: They are quick to adopt and adapt to new technologies, driving digital transformation within organizations.
- Emphasis on Continuous Learning: They engage in continuous learning to stay updated with technological advancements and industry trends.
Strategies for Effective Management
Operational leaders can adopt the following strategies to better manage and engage the younger workforce:

1. Embrace Technology and Innovation
Action Points:
- Implement Modern Tools: Introduce advanced manufacturing technologies such as automation, IoT, and AI to streamline operations.
- Training and Development: Provide training programs to enhance technological skills and ensure that both older and younger employees can work seamlessly with new technologies.
Benefits:
- Increased efficiency and productivity.
- Enhanced employee satisfaction by aligning with their tech-savviness.
2. Foster a Flexible Work Environment
Action Points:
- Flexible Scheduling: Allow for flexible work hours and remote work options where possible.
- Work-Life Integration: Promote policies that support work-life balance, such as mental health days and flexible leave policies.
Benefits:
- Higher job satisfaction and reduced burnout.
- Improved retention rates.
3. Create a Culture of Open Communication
Action Points:
- Regular Check-ins: Conduct regular one-on-one meetings to provide feedback and discuss career development.
- Transparent Communication: Maintain open lines of communication about company goals, challenges, and successes.
Benefits:
- Better alignment with company goals.
- Increased trust and loyalty among employees.
4. Align Work with Purpose and Values
Action Points:
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Engage in CSR activities that resonate with the workforce’s values.
- Purpose-Driven Projects: Assign projects that have a clear impact and contribute to the company’s mission.
Benefits:
- Enhanced motivation and commitment.
- Stronger connection to the company’s mission.
5. Provide Continuous Learning and Development
Action Points:
- Skill Development Programs: Offer continuous learning opportunities through workshops, courses, and certifications.
- Mentorship Programs: Establish mentorship programs pairing younger employees with experienced leaders.
Benefits:
- Better skill sets and adaptability to change.
- Increased job satisfaction and career growth.
Practical Steps for Implementation
Engage in Active Listening
Operational leaders should prioritize listening to their younger employees’ concerns and suggestions. This can be done through:
- Surveys and Feedback Forms: Regularly distribute surveys to gather insights on employee satisfaction and areas for improvement.
- Focus Groups: Conduct focus group discussions to delve deeper into specific issues and develop targeted solutions.
Promote Inclusivity and Diversity
Fostering an inclusive and diverse workplace is crucial. Steps to achieve this include:
- Diversity Training: Provide training on diversity, equity, and inclusion to all employees.
- Inclusive Hiring Practices: Ensure hiring practices are unbiased and focus on diverse talent pools.
Encourage Cross-Generational Collaboration
Encouraging collaboration between different generations can bridge the gap. Strategies include:
- Mixed-Age Teams: Create teams with a mix of younger and older employees to leverage diverse perspectives.
- Knowledge Sharing Sessions: Organize sessions where experienced employees share their expertise and younger employees introduce new technologies and trends.
Addressing Resistance to Change
Operational leaders who are resistant to change must be supported through:
- Leadership Training: Provide training focused on modern management practices and the benefits of a flexible, inclusive work environment.
- Change Management Programs: Implement change management programs to ease the transition and help leaders adapt to new practices.

Indian Business Leaders and Organizations Embracing Modern Workforce Management
Several Indian business leaders and organizations have recognized the evolving needs and expectations of the younger workforce and have adopted similar strategies to manage and engage them effectively. Here are some notable examples:
1. N. Chandrasekaran, Tata Sons
N. Chandrasekaran, the Chairman of Tata Sons, has been vocal about the importance of digital transformation and innovation within the Tata Group. Under his leadership, Tata companies have increasingly adopted new technologies and flexible work practices to stay relevant and competitive.
Key Initiatives:
- Digital Transformation: Tata Steel, under Tata Group, has implemented advanced technologies like IoT and AI to enhance efficiency and productivity.
- Flexible Work Policies: Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) introduced the “25/25 model,” which allows 25% of the workforce to work from home by 2025.
2. Rajesh Gopinathan,Ex- TCS
Rajesh Gopinathan,Ex- CEO and Managing Director of TCS, had been a strong advocate for innovation and employee well-being. He emphasized the importance of creating a supportive work environment that fosters continuous learning and development.
Key Initiatives:
- Continuous Learning: TCS has a robust learning and development program called TCS Elevate, which provides employees with opportunities to upskill and reskill.
- Mental Health Support: TCS offers comprehensive mental health resources, including counseling services and wellness programs.
3. Harsh Mariwala, Marico
Harsh Mariwala, Chairman of Marico, has highlighted the importance of an inclusive culture and the need for leaders to adapt to the changing workforce dynamics. Marico focuses on building a purpose-driven and innovative work environment.
Key Initiatives:
- Inclusive Culture: Marico fosters an inclusive workplace through diverse hiring practices and inclusive policies.
- Employee Engagement: The company emphasizes employee engagement through initiatives that align with the workforce’s values and aspirations.
4. Anand Mahindra, Mahindra Group
Anand Mahindra, Chairman of Mahindra Group, has been a proponent of integrating technology and promoting a work-life balance. He believes in empowering employees and creating a work environment that aligns with their personal and professional goals.
Key Initiatives:
- Technology Integration: Mahindra Group has embraced digital tools and platforms to enhance productivity and innovation.
- Work-Life Balance: The group offers flexible working hours and remote work options to support work-life balance.
5. Infosys
Infosys, under the leadership of Salil Parekh, has been a pioneer in adopting modern work practices to meet the expectations of the younger workforce.
Key Initiatives:
- Learning and Development: Infosys’ Lex platform provides continuous learning opportunities for employees to stay updated with the latest industry trends and technologies.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Infosys promotes a diverse and inclusive work culture, ensuring equal opportunities for all employees.
Conclusion
The strategies discussed are indeed applicable in the Indian context and have been effectively implemented by various business leaders and organizations. These examples demonstrate that adopting modern management practices, embracing technology, fostering an inclusive culture, and prioritizing employee well-being can significantly enhance the engagement and productivity of the younger workforce in India. Understanding and addressing the needs of the younger workforce not only improves their satisfaction and productivity but also drives the overall success and innovation within the organization. Operational leaders in manufacturing and supply chain sectors must adapt to these changes to manage and engage the younger workforce effectively, ensuring sustainable growth and competitiveness.
Good luck
Karthik
18/6/24 1130am.

