#194

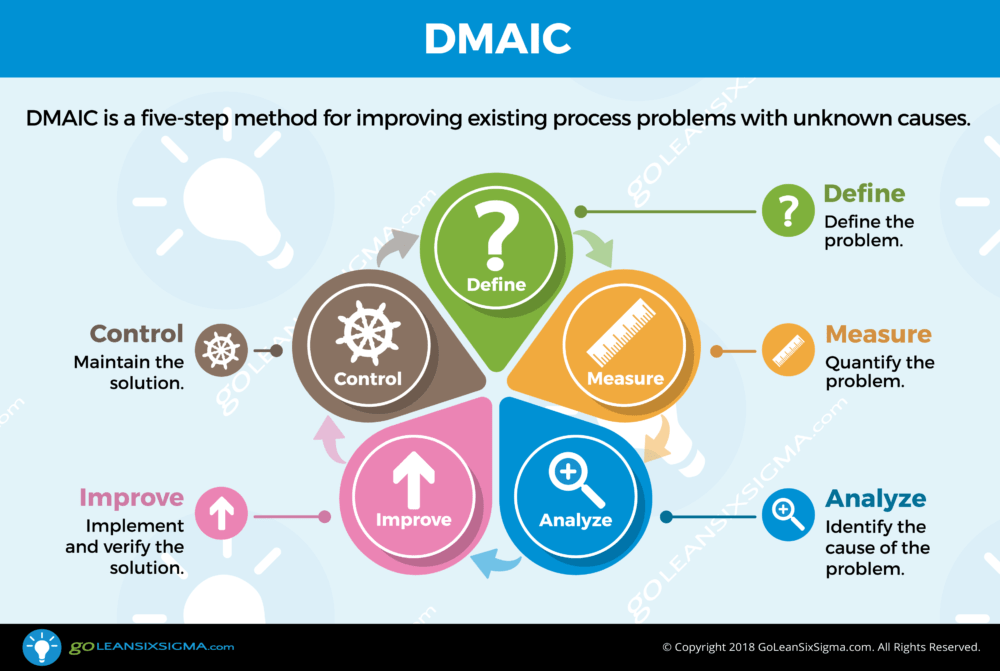
Introduction
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, ensuring workplace safety while maintaining efficiency is paramount. Lean Manufacturing, with its focus on waste reduction and process optimization, Standardisation as well as Rapid problem solving, offers a unique opportunity to enhance safety measures in the workplace. This blog explores how integrating Lean Manufacturing principles can significantly boost safety, creating a proactive and responsive work environment.
Understanding Lean Manufacturing Principles
Lean Manufacturing is a systematic approach to minimizing waste ( Resources, Time, Commodity) without sacrificing productivity. Its core principles include:
- Value: Identifying what is valuable to the customer.
- Value Stream: Mapping out the steps that add value.
- Flow: Ensuring a smooth, uninterrupted workflow. (Linear Flow)
- Pull: Producing based on demand.
- Perfection: Continuously improving processes.
These principles aim to eliminate waste and improve efficiency, which can also lead to a safer workplace.
The Synergy Between Lean and Safety
Lean principles and safety initiatives share a common goal: creating an efficient and hazard-free environment. The concept of “Lean Safety” emphasizes the integration of Lean tools with safety measures, promoting a culture of continuous improvement in safety.
Lean Tools and Their Impact on Safety
5S (Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain)
- Sort: Remove unnecessary items to reduce clutter.
- Set in Order: Organize tools and materials for easy access.
- Shine: Clean the workspace to identify and address potential hazards.
- Standardize: Establish standards for cleanliness and organization.
- Sustain: Maintain these standards through regular audits.
Kaizen (Continuous Improvement)
- Involve employees in identifying safety risks and proposing improvements.
- Small, incremental changes can significantly reduce accident rates.
Value Stream Mapping
- Visualize the entire process to identify and eliminate potential safety hazards.
Kanban
- Implement a pull system to avoid overproduction and reduce the risk of handling excessive inventory.
Poka-Yoke (Error Proofing)
- Use mistake-proofing techniques to prevent human errors that could lead to accidents.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Consider the case of a major automotive manufacturer in India. By implementing 5S and Kaizen, they not only improved their workflow but also saw a 30% reduction in workplace accidents. Employees reported a cleaner, more organized environment, leading to fewer slip and trip incidents.
In 2010, I embarked on a Lean Six Sigma project as an EHS professional, aiming to reduce the variance between self-assessment on EHS done by sites and corporate safety audits which the site undergoes. With over 100 global sites in our supply chain, we observed that 95% of the sites had a significant variance of around 30% in their self-assessment scores, often skewed unfavorably. This was unacceptable, as sites tended to overrate their EHS performance, leading to nasty surprises during corporate audits of unacceptable low Audit scores.
To address this, my team and I developed a tool-based validation system, establishing clear guidelines, norms, and evidence requirements for site self-assessments. This approach, rooted in Lean thinking, led to the total elimination of deviations and ensured that there were no more unpleasant surprises. The successful implementation of this project underscored the power of Lean principles in driving consistent and reliable safety assessments.
Implementing Lean Safety in Your Organization
- Leadership Commitment: Ensure top management is committed to Lean Safety.
- Employee Involvement: Engage employees at all levels to foster a culture of safety.
- Training: Conduct regular training sessions on Lean tools and safety protocols.
- Sustainability: Regular audits and continuous improvement initiatives are crucial.
Measuring the Impact
To gauge the effectiveness of Lean Safety, track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as:
- Incident rates
- Near-miss reports
- Employee feedback
- Safety audit scores
- Safety Metric Scores.
These metrics can help you assess improvements and identify areas needing further attention.
Challenges and Solutions
Common challenges in implementing Lean Safety include resistance to change and insufficient training. Overcome these by:
- Communicating the benefits of Lean Safety clearly.
- Providing comprehensive training and resources.
- Encouraging feedback and suggestions from employees.
- Matured EHS systems and committed Safety professionals.
Future Trends in Lean Safety
With Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing on the rise, integrating advanced technologies like IoT and AI can further enhance Lean Safety. These technologies can provide real-time data, predictive analytics, and automated safety interventions, making workplaces even safer.
Conclusion
Integrating Lean Manufacturing principles with safety initiatives (Standardized work, Error Proofing) can lead to significant improvements in workplace safety. By adopting Lean Safety, organizations can create a safer, more efficient, and more productive environment. Let’s embrace this approach and work towards a safer future.

Call to Action
What has been your experience with Lean Manufacturing and safety? Share your insights and stories in the comments below. For more information on implementing Lean Safety in your organization, feel free to contact me. Let’s work together to create safer workplaces.
Regards
Karthik. 23/6/24 11am.

