#195.
I was away on Business travel for a week, back late evening, yesterday, so the blog resumes.
1 Introduction
In the dynamic world of workplace safety, Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) has always been a critical line of defense. Traditionally, hard hats, gloves, goggles, and vests have played pivotal roles in safeguarding workers from harm. However, the advent of smart wearables is revolutionizing the PPE landscape, integrating technology to enhance safety, efficiency, and overall worker well-being. We explores the latest trends, advancements, innovations, and benefits of smart PPE.
2 Overview of PPE
Definition: Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) refers to protective gear designed to safeguard workers from hazards that can cause injuries or illnesses. PPE includes items like helmets, gloves, eye protection, high-visibility clothing, and safety footwear.
Traditional PPE: Traditional PPE has been effective in reducing workplace injuries and fatalities. Items such as hard hats, safety goggles, and gloves provide basic protection against physical, chemical, and biological hazards.
Importance: PPE is essential in preventing workplace injuries and ensuring compliance with safety regulations. It forms a critical component of occupational safety strategies across various industries.
3 Evolution of PPE: From Traditional to Smart Wearables
Historical Perspective: The development of PPE has evolved significantly over the decades, from simple protective gear to more sophisticated equipment. Initially, PPE was designed primarily for physical protection without technological integration.
Technological Integration: With advancements in technology, PPE has evolved into smart wearables. These innovative devices incorporate sensors, connectivity, and data analytics, offering enhanced protection and real-time monitoring capabilities.
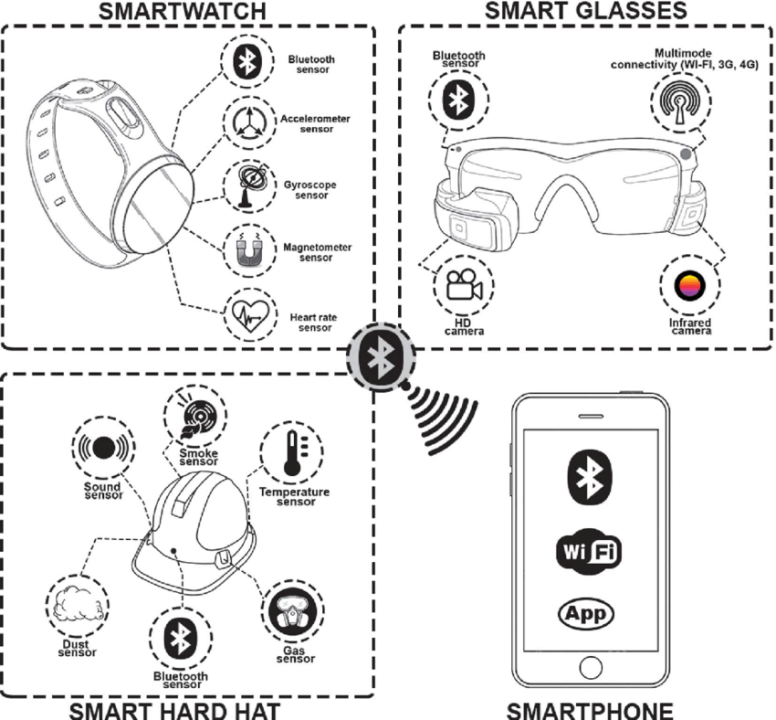 4 Latest Trends in Smart Wearables for PPE: Real Use Examples
4 Latest Trends in Smart Wearables for PPE: Real Use Examples
IoT Integration
Example: Honeywell Connected Worker Honeywell’s Connected Worker solution integrates IoT-enabled smart PPE to provide real-time monitoring and data collection. Workers wear devices that track various parameters, such as exposure to toxic gases, noise levels, and heart rate. This data is transmitted to a central system where it can be analyzed and acted upon immediately. For example, if a worker’s environment reaches dangerous levels of toxic gas, an alert is sent to both the worker and the safety team, enabling quick evacuation or intervention.
Impact: This integration enhances situational awareness and decision-making by providing a constant flow of data that can be used to prevent accidents and respond to emergencies more effectively.
Biometric Sensors
 Example: Kenzen Smart PPE Kenzen has developed a wearable device that monitors biometric data such as heart rate, body temperature, and hydration levels. This smart PPE is particularly useful in industries where workers are exposed to extreme heat or physically demanding tasks. For instance, construction workers wearing Kenzen devices can receive alerts when their body temperature reaches a critical threshold, prompting them to take breaks and hydrate.
Example: Kenzen Smart PPE Kenzen has developed a wearable device that monitors biometric data such as heart rate, body temperature, and hydration levels. This smart PPE is particularly useful in industries where workers are exposed to extreme heat or physically demanding tasks. For instance, construction workers wearing Kenzen devices can receive alerts when their body temperature reaches a critical threshold, prompting them to take breaks and hydrate.
Impact: By detecting signs of fatigue, stress, and other health-related issues early, biometric sensors help in preventing heat stress, dehydration, and other conditions that could lead to serious health problems or accidents.
Augmented Reality (AR)


Example: DAQRI Smart Helmet The DAQRI Smart Helmet is an AR-enabled device that provides workers with real-time information overlays. For example, a maintenance worker wearing the DAQRI helmet can see virtual instructions and diagrams superimposed on their field of view, helping them perform complex repairs more accurately. Hazard alerts and safety instructions can also be displayed directly on the helmet’s visor.
Impact: AR technology in PPE improves situational awareness and operational efficiency by delivering critical information directly to the worker’s line of sight, reducing the need to look away or consult separate manuals.
GPS and Location Tracking
![]() Example: SolePower Smart Boots SolePower has developed smart boots with integrated GPS tracking that monitor the location and movements of workers in real-time. These boots are particularly useful in large construction sites or remote areas where workers might be at risk of getting lost or encountering hazards. In the event of an emergency, the boots can help locate and rescue workers quickly.
Example: SolePower Smart Boots SolePower has developed smart boots with integrated GPS tracking that monitor the location and movements of workers in real-time. These boots are particularly useful in large construction sites or remote areas where workers might be at risk of getting lost or encountering hazards. In the event of an emergency, the boots can help locate and rescue workers quickly.
Impact: GPS-enabled smart PPE ensures precise tracking of worker locations, enhancing safety by enabling quick response during emergencies and improving overall workforce management.
Smart Clothing

Example: Hexoskin Smart Shirts Hexoskin offers smart shirts embedded with sensors that can monitor vital signs such as heart rate, respiratory rate, and activity levels. These shirts are used in various industries, including mining and manufacturing, where workers are exposed to hazardous conditions. The sensors can detect environmental hazards like extreme temperatures or harmful chemicals and send immediate alerts to both the wearer and safety personnel.
Impact: Smart clothing provides continuous monitoring and immediate alerts, allowing for prompt action to prevent exposure to harmful conditions. This enhances worker safety by addressing potential hazards before they can cause harm.
Inference.
The integration of smart wearables in PPE is revolutionizing workplace safety by leveraging advanced technologies such as IoT, biometric sensors, AR, GPS, and smart fabrics. These innovations provide real-time data collection, enhanced situational awareness, and immediate alerts, significantly improving the safety and efficiency of workers in various industries. As these technologies continue to evolve, their impact on workplace safety will only grow, making smart PPE an essential component of modern occupational safety strategies.
5 Innovations in Different Types of Smart PPE
Smart Helmets: Equipped with AR displays, noise-cancellation features, and integrated communication systems, smart helmets enhance both safety and productivity. They provide workers with critical information without requiring them to look away from their tasks .
Smart Glasses/Goggles: These devices offer real-time data display, eye protection, and navigation assistance. They are particularly useful in complex and dynamic work environments where quick access to information is crucial .
Smart Gloves: Featuring sensors that can detect hazardous substances, ergonomic designs, and gesture controls, smart gloves provide enhanced protection and functionality. They allow workers to interact with their environment more effectively while remaining protected .
Smart Vests and Clothing: Smart vests and clothing come with sensors that monitor body temperature, heart rate, and environmental conditions. These wearables ensure that workers’ health parameters are continuously monitored, preventing accidents due to fatigue or heat stress .
Smart Boots: Smart boots are designed with features such as fall detection, pressure monitoring, and GPS tracking. These boots ensure that workers’ movements are tracked, and any abnormal activities are immediately reported .
6 Benefits of Smart Wearables in PPE
Enhanced Safety: Real-time monitoring and alerts enable immediate response to potential hazards, significantly reducing the risk of injuries and fatalities .
Increased Efficiency: Smart wearables improve workflow and communication, allowing workers to perform their tasks more efficiently and safely .
Proactive Maintenance: Predictive maintenance capabilities allow for early detection of equipment failures, ensuring that issues are addressed before they lead to accidents .
Better Compliance: Smart PPE facilitates easier tracking of safety compliance and documentation, helping organizations meet regulatory requirements .
Worker Well-being: Monitoring health parameters ensures that workers remain healthy and prevents fatigue-related accidents. This proactive approach enhances overall worker well-being and productivity .
7 Industry Examples
Construction Industry:
Case Study: Turner Construction Company
Turner Construction Company implemented smart PPE across its various construction sites to enhance safety and efficiency. Workers were equipped with smart helmets that integrated AR technology, providing real-time data overlays for safety instructions, project blueprints, and hazard alerts. This allowed workers to maintain focus on their tasks while staying informed about potential risks. GPS tracking in the helmets ensured precise location monitoring, crucial for managing large construction sites and ensuring quick response during emergencies.
Impact: Turner Construction reported a significant reduction in workplace accidents due to improved situational awareness and adherence to safety protocols. The integration of smart PPE also streamlined communication among workers and supervisors, enhancing overall project efficiency.
Oil and Gas Industry:
Case Study: BP
BP implemented smart PPE solutions in its offshore drilling operations to monitor worker health and safety in real-time. Biometric sensors embedded in clothing and helmets tracked vital signs such as heart rate, body temperature, and exposure to toxic gases. This data was transmitted to a centralized control room where safety personnel could monitor conditions and intervene when necessary. AR-enabled goggles provided workers with virtual displays of equipment status, procedural guidelines, and emergency protocols.
Impact: The adoption of smart PPE by BP led to a significant decrease in incidents related to heat stress, exposure to hazardous chemicals, and equipment malfunction. Workers reported increased confidence in their safety, contributing to higher job satisfaction and productivity.
Manufacturing Industry:
Case Study: Toyota
Toyota integrated smart PPE into its manufacturing processes to enhance worker safety and operational efficiency. Smart gloves equipped with sensors allowed workers to handle hazardous materials safely by detecting chemical leaks and monitoring environmental conditions. The gloves provided real-time feedback to workers and supervisors, enabling quick response to potential hazards. Additionally, smart vests with biometric sensors tracked workers’ physical exertion and fatigue levels, ensuring timely breaks and reducing the risk of musculoskeletal injuries.
Impact: Toyota observed a decrease in workplace injuries and illnesses among its manufacturing staff, attributed to better hazard awareness and proactive safety measures enabled by smart PPE. The implementation also contributed to smoother workflow management and improved employee morale.
Success Stories
Reduced Accident Rates:
Example: Intel Corporation
Intel Corporation implemented smart PPE across its semiconductor manufacturing facilities to address safety concerns related to chemical exposure and ergonomic risks. Smart clothing embedded with sensors monitored environmental conditions and alerted workers to potential hazards. This proactive approach significantly reduced the number of accidents related to chemical spills and ergonomic strains, ensuring a safer working environment for employees.
Improved Worker Satisfaction:
Example: Boeing
Boeing introduced smart wearables in its aircraft assembly plants to improve worker satisfaction and efficiency. AR-enabled glasses provided assembly technicians with digital overlays of assembly instructions and quality checks, reducing errors and enhancing productivity. Real-time communication through smart helmets facilitated quick troubleshooting and decision-making, leading to smoother operations and higher job satisfaction among workers.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency:
Example: General Motors (GM)
General Motors integrated smart PPE in its automotive manufacturing plants to optimize operational efficiency and ensure worker safety. GPS-enabled vests tracked the movement of assembly line workers, facilitating better workflow management and resource allocation. Biometric sensors in gloves and helmets monitored worker health and fatigue levels, prompting timely breaks and reducing production disruptions. These initiatives contributed to streamlined processes and improved overall plant performance.
Inference.
These case studies and success stories highlight the tangible benefits of smart wearables in PPE across diverse industries. From construction and oil and gas to manufacturing, organizations have successfully leveraged advanced technologies to enhance safety, reduce accidents, improve worker satisfaction, and boost operational efficiency. As smart PPE continues to evolve with innovations in IoT, biometrics, AR, and GPS technologies, its role in shaping the future of workplace safety remains pivotal.
8 Challenges and Future Directions
Challenges: Despite the benefits, adopting smart PPE comes with challenges, including high costs, integration issues, and data privacy concerns .
Future Trends: The future of smart PPE is promising, with ongoing advancements in technology expected to bring even more innovative solutions. Trends such as enhanced AI capabilities, improved sensor technology, and greater interoperability are anticipated .
Conclusion
Smart wearables are revolutionizing the PPE landscape, offering unprecedented levels of protection, efficiency, and worker well-being. As technology continues to evolve, the adoption of smart PPE will become increasingly crucial in ensuring workplace safety. Organizations are encouraged to embrace these innovations to create safer and more productive work environments.
Karthik
30th June 2024, 1pm.


