#236
It is the End of the year to take stock of EHS performance. Most sites across the world, would have the same issue, thanks to very poor or no regulatory mechanism / inspection, things go scot free.
OSHA Citations ( Reproduced from CBIZ.com).

2024’s Top Ten OSHA Safety Violations
1. Fall Protection Infractions: A Critical Concern (6,307 citations)
For over a decade, fall protection violations have been a recurring concern. According to the Bureau of Labor and Statistics, 80% of construction fatalities result from falls. The risks associated with unstable working surfaces, improper ladder usage and neglecting fall protection measures are more than cause for alarm. They can lead to tragic accidents and serious injuries that impact workers’ lives and business operations.
Key Preventive Tips:
- Immediately cover any holes on the floor.
- Construct floor hole covers that can support double the weight of workers, equipment and materials.
- Prioritize and regularly inspect and maintain fall protection systems (e.g., guardrails, nets, harnesses) to ensure they are in good working condition.
- Use personal fall arrest systems (PFAS) when working at heights above six feet, ensuring they are correctly fitted and anchored.
2. Hazard Communication: Essential Information for Workers (2,888 citations)
Even if your team doesn’t directly handle chemicals, exposure or proximity to hazardous materials still poses risks. Maintaining a secure work environment ensures workers understand how to handle chemicals properly. Effective hazard communication allows employees to identify chemicals correctly, understand lurking dangers and take necessary safety precautions. Additionally, employees must have access to updated safety data sheets (SDS), receive label training and be informed about newly identified hazards.
Key Preventive Tips:
- Ensure workers are informed about chemicals they might encounter or be exposed to.
- identify the location of SDSs
- Educate employees on the proper and improper use of workplace chemicals.
- Train staff on the appropriate emergency spill procedures.
3. Ladder Safety: Addressing a Common Citation (2,573 citations)
While ladders are often considered a trusted safety tool, they have unfortunately become a treacherous foe. The American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons reports each year 500,000 people are treated for ladder-related injuries with 300 of these incidents turning fatal. Many of these incidents stem from violations of basic ladder safety rules.
Key Preventive Tips:
- Never exceed the ladder’s maximum load rating (user plus materials) and only allow one person on a ladder at a time.
- Always maintain a centered position between the ladder rails, avoiding overreaching or leaning too far to the side while working. If necessary, descend from the ladder and reposition it.
- Refrain from stepping on the top step, bucket shelf or attempting to climb or stand on the rear section of a stepladder.
- Face the ladder when climbing up or down and never leave a raised ladder unattended.
- If you feel dizzy or tired, carefully descend from the ladder.
- Wear non-slip footwear whenever using a ladder to prevent accidents.
4. Respiratory Protection: Safeguarding Worker Health (2,470 citations)
Even the tiniest particles and contaminants can have a big impact on health, both in the short term and the long term. That’s why it’s crucial to protect from these dangers. Respirators shield employees from areas with insufficient oxygen, harmful dust, fog, smoke, mists, gases, vapors and sprays. By wearing respirators, workers can avoid potential hazards that could lead to serious consequences (e.g., cancer, lung problems, death).
Key Preventive Tips:
- Only use certified respirators designed to protect against the specific contaminant you are working with.
- Before using, carefully inspect respirators for signs of damage and promptly repair or replace the respirator.
- Always ensure a proper facepiece seal to guarantee a secure seal.
- Maintain a clean-shaven face to ensure a proper seal and avoid any interference with the respirator.
- Keep track of your respirator to avoid inadvertently utilizing another employee’s respirator.
- Stay updated with regular training on proper usage and maintenance of respirators and seek assistance when needed.
5. Lockout/Tagout Procedures: Preventing Machinery Accidents (2,443 citations)
Imagine the dire consequences if a machine were suddenly activated while someone was inside. Prevent such horrific accidents by actively controlling hazardous energy in machinery through lockout procedures. This involves securely locking and rendering the machine energy sources non-operational. The practice of tagout serves as a visual reminder to employees, communicating with clear warnings that the machinery shouldn’t be used. Lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures are invaluable in ensuring energy controls stay in an off or safe position during maintenance and service work.
Key Preventive Tips:
- Consistently secure energy control devices using assigned lock keys.
- If you install a lock, ensure you’re the one who removes it.
- Clearly label the locks you install with durable tags that identify them as yours.
- Never lend or share locks, combinations or keys with anyone else.
- Prioritize shift change safety by ensuring new workers apply their locks before removing yours.
- Before working on any equipment, ensure that all energy is completely dissipated.
- Verify that all LOTO devices are compatible with the specific environment in which they will be used.
- Thoroughly test the machine or system before starting work to ensure there isn’t remaining energy that could cause harm.
6. Powered Industrial Trucks (PIT): Ensuring Safe Operation (2,248 citations)
PIT vehicles such as fork trucks, platform trucks and motorized hand trucks are invaluable for material handling. However, it’s crucial to stress that untrained and unauthorized employees should never operate them. OSHA mandates proper training and certification for PIT operators to prevent accidents and injuries.
Key Preventive Tips:
- Maintain clear driving paths by removing any obstructions.
- Exercise caution when approaching corners, blind spots and doorways by reducing speed.
- Embrace defensive driving by remaining aware of your surroundings and anticipating the unexpected.
- Avoid making turns on inclined surfaces.
- Cross tracks diagonally and reduce speed when encountering uneven floors and surfaces.
- Ensure all limbs and extremities remain inside the truck.
- Always prioritize pedestrian safety by giving them the right of way.
7. Fall Protection Training: Meeting OSHA Requirements (2,050 citations)
Ensure employee safety for those at risk of falling hazards by providing comprehensive fall protection training. This program equips workers with the knowledge to identify potential fall hazards and implement appropriate measures to mitigate risks. OSHA mandates employers ensure workers understand how to use fall protection equipment property and recognize unsafe workplace conditions.
Key Preventive Tips:
- Provide comprehensive training to all employees at risk of fall hazards.
- Equip employees with the knowledge to identify fall hazards and implement appropriate measures to mitigate risks.
- Offer training as needed to keep employees up to date with fall protection procedures.
8. Scaffolding Safety: Key Compliance Issues (1,873 citations)
Scaffolding, while essential for many construction projects, harbors one primary peril—falling. That’s why it’s crucial to establish proper scaffolding setup, training and procedures to comply with OSHA standards. Not only does scaffolding ensure the safety of employees but also protects innocent bystanders.
Key Preventive Tips:
- Conduct daily inspections to identify and eliminate potential slipping hazards on all walking and working surfaces.
- Always follow the guidance of a qualified individual when moving, dismantling or altering a scaffold.
- Never move a scaffold with workers still on it.
- Ensure scaffold loads remain within the specified capacity and remove equipment when not in use.
- Stay vigilant and be aware of adverse weather conditions as high winds, rain and snow can pose risks at elevated heights.
9. Eye & Face Protection: Required Safety Measures (1,814 citations)
To comply with OSHA regulations, employers must conduct personal protective equipment (PPE) training for workers. It’s important to obtain written confirmation from each employee regarding their attendance and understanding of the training. Employers are responsible for providing and paying for OSHA-mandated PPE including the replacement for normal wear and tear.
Key Preventive Tips:
- Equip all affected employees with appropriate eye and face protection when exposed to flying particles or other hazardous situations.
- Provide suitable PPE to safeguard employees.
- Ensure that the provided PPE is well-designed, properly maintained and comfortable to wear.
- Conduct thorough training to educate employees on the proper use of PPE.
10. Machine Guarding: Protecting Employees from Hazards (1,541 citations)
Machine guards are made to shield employees who work with perilous equipment. Employers must provide this protection, keeping operators and those near the machine safe from all kinds of hazards (e.g., nip points, rotating parts, flying chips, sparks). Adhering to OSHA guidelines regarding machine guarding not only helps prevent workplace injuries but also fosters a culture of safety within the organization.
Key Preventive Tips:
- Never adjust or remove a guard without explicit permission from a supervisor or unless the adjustment is routine and an accepted part of your job.
- Machinery shouldn’t be operated without ensuring all guards are properly in place.
- If guards are missing or defective, promptly notify a supervisor.
- Power off the machine and lock and tag the main switch before detaching guards for maintenance or adjustment.
- Avoid wearing loose clothing, jewelry or allowing long hair to be unsecured around mechanical equipment.
Importance of Coverage & Risk Management Strategies
To effectively address these violations, companies must secure appropriate insurance coverage to safeguard against employee injuries and penalties. Comprehensive insurance solutions, like general liability and workers’ compensation, can protect your organization from financial repercussions due to accidents or compliance issues.
Additionally, collaborating with risk management professionals can yield customized risk management plans designed for your industry and operational requirements. These specialists can perform risk assessments and provide insights on best practices, minimizing the likelihood of OSHA inspections and associated fines. By prioritizing strong safety protocols and comprehensive insurance, you can protect both your workforce and your finances.
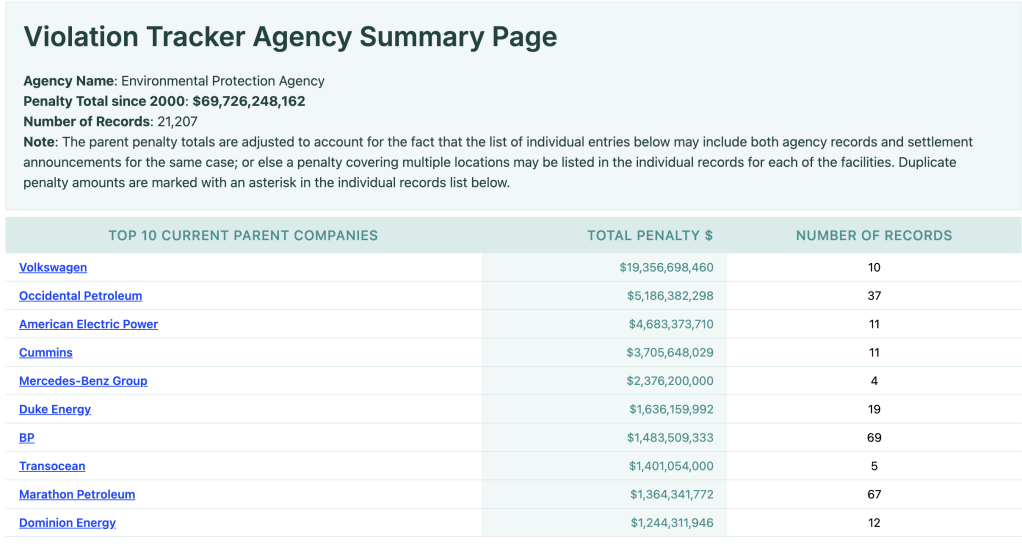
EPA:-
EPA has collected 69Bn $ penalty so far from year 2000. Volkswagen leads the list with 19Bn$ paid in penalty.
In 2024, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) identified several significant compliance violations across various industries. These cases highlight the ongoing challenges in environmental compliance and underscore the importance of stringent oversight. Here are ten notable violations from that year:
- Tesla’s Environmental Violations: Tesla faced scrutiny for multiple environmental infractions, including hazardous waste mismanagement and air quality permit breaches at its Fremont, California, facility. The company settled with California authorities, agreeing to pay $1.5 million and implement corrective measures.
- General Motors’ Excess Emissions: General Motors was penalized $145.8 million after an investigation revealed that approximately 5.9 million vehicles from the 2012-2018 model years emitted over 10% more carbon dioxide than initially reported. The settlement also required GM to forfeit significant carbon allowances and fuel economy credits.
- Marathon Oil’s Air Pollution Settlement: Marathon Oil agreed to a $241 million settlement for air pollution violations at facilities on North Dakota’s Fort Berthold Indian Reservation. This included a record $64.5 million penalty and $177 million allocated for environmental upgrades to reduce emissions.
- Philadelphia Energy Solutions Refinery Explosion: Following a 2019 explosion and fire at its Philadelphia refinery, Philadelphia Energy Solutions reached a $4.2 million settlement with the EPA in 2024. The incident was attributed to inadequate risk assessment and equipment maintenance.
- Illegal Emissions Control Bypass Devices: Federal prosecutors charged auto-parts dealers involved in a $74 million scheme to sell devices that allowed diesel truck drivers to deactivate emissions control systems, leading to increased pollution.
- Red Dog Mine Hazardous Waste Violations: The operators of Alaska’s Red Dog Mine agreed to pay over $429,794 to the EPA for hazardous waste violations occurring between October 2019 and January 2024, marking the largest violation in the mine’s history.
- ADCO Constructions’ Water Pollution Fine: ADCO Constructions was fined $30,000 by the New South Wales Environment Protection Authority for discharging sediment-laden water into Curl Curl Creek, threatening the habitat of the critically endangered Climbing Galaxias fish.
- EPA’s Action Against Denka Performance Elastomer: The EPA filed a complaint against Denka Performance Elastomer, alleging that its LaPlace, Louisiana, plant posed an imminent danger to public health due to emissions of cancer-causing chloroprene.
- eBay’s Environmental Violations: The U.S. Department of Justice filed a complaint against eBay for facilitating the sale of products that violated environmental laws, including illegal pesticides and devices that bypass vehicle emissions controls.
- Michael Hart’s Illegal Importation of Greenhouse Gases: Michael Hart was arrested for smuggling hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) into the U.S. from Mexico without proper authorization, violating the American Innovation and Manufacturing Act of 2020.
These cases underscore the critical need for robust environmental compliance programs and vigilant enforcement to protect public health and the environment.
Penalty are money poured in to drain and affects P&L. Proactive /vigilant compliance reduces this, thus helping to bottomline.
Karthik.
27/11/24.

